Topographic Mapping
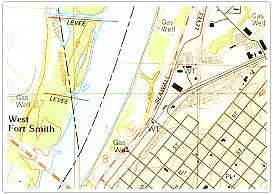
One of the most widely used of all maps is the topographic map. The feature that most distinguishes topographic maps from maps of other types is the use of contour lines to portray the shape and elevation of the land. Topographic maps render the three-dimensional ups and downs of the terrain on a two-dimensional surface.
Topographic maps usually portray both natural and man made features. They show and name works of nature including mountains, valleys, plains, lakes, rivers, and vegetation. They also identify the principal works of man, such as roads, boundaries, transmission lines, and major buildings.
The wide range of information provided by topographic maps make them extremely useful to professional and recreational map users alike. Topographic maps are used for engineering, energy exploration, natural resource conservation, environmental management, public works design, commercial and residential planning, and outdoor activities like hiking, camping, and fishing.
Topographic maps are different from other maps because they show the shape and elevation of features of landscape such as mountains and valleys. Here, you will investigate what the elements of a topographic map are, and how they are used.
Topographic mapping is a vital resource for a wide range of applications including:
- emergency and disaster response,
- national defence,
- asset and facilities management,
- demographics analysis,
- environmental monitoring,
- mineral and energy exploration,
- fleet and logistics management,
- graphic presentation of thematicdata,
- infrastructure planning,
- other map production,
- market analysis, navigation and positioning,
- route planning,
- risk assessment,
- surveillance, and
- teaching.
 |
 |










